Though blood pressure reduction is the prime target, ensuring a lower risk of metabolic disturbances is equally important.
Hyponatremia significantly worsens the prognosis of patients with different chronic diseases. In patients with arterial hypertension, the risk of hyponatremia is 1.5 times higher than in the general population.1 .
Potassium imbalances can lead to arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Maintaining levels between 4.1 and 4.7 mmol/L is crucial to reduce mortality risk.2
Antihypertensive therapy is often associated with the induction of new-onset diabetes (NOD), which further complicates the CVD risks.3
Hydrochlorothiazide is associated with reduced risks of Type 2 Diabetes as well as metabolic imbalances, notably Hyponatremia
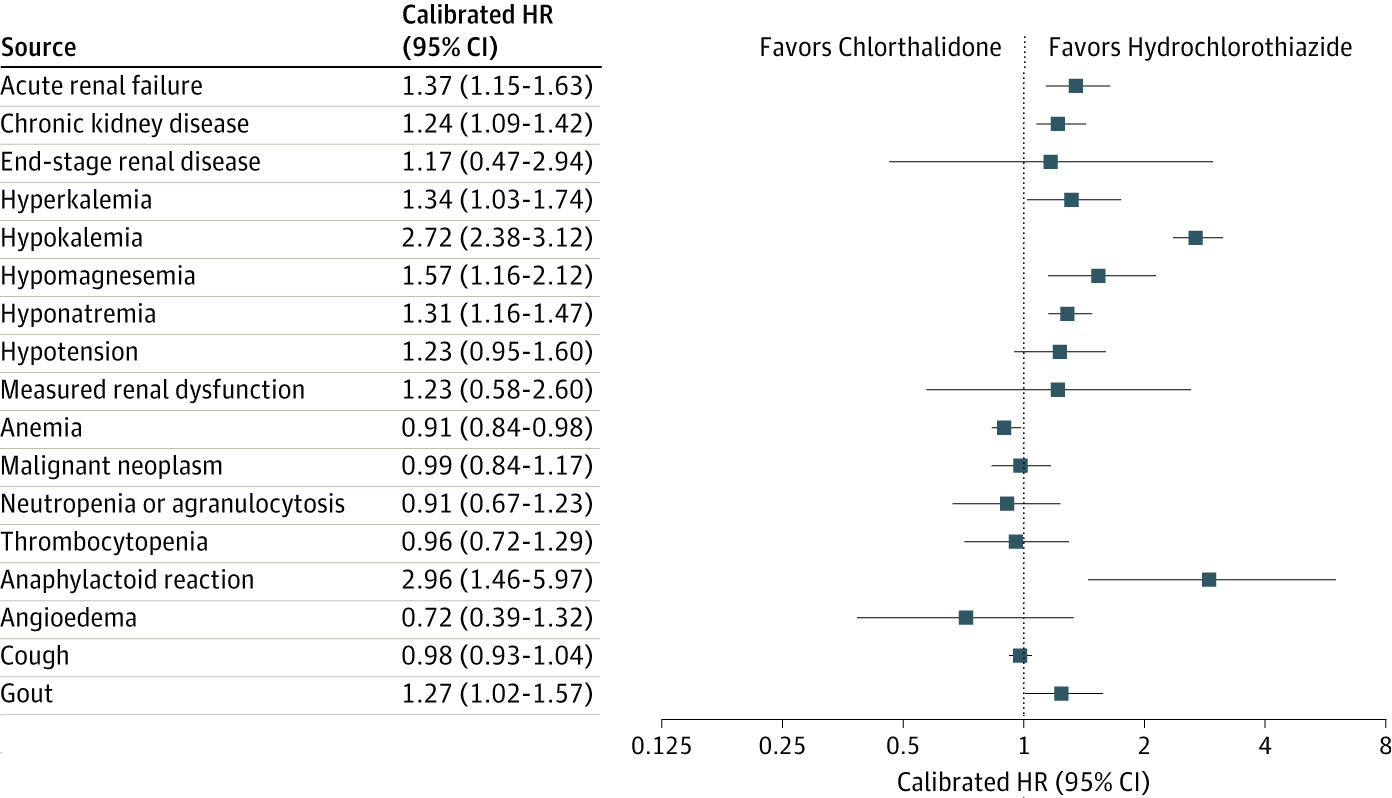
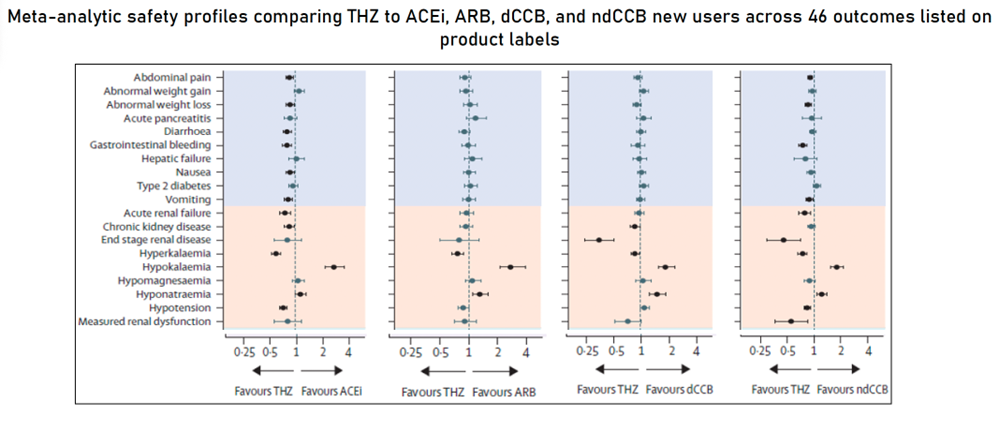
LEGEND-HTN Safety profiles favoured thiazide or thiazide-like diuretics over angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in terms of Hyperkalaemia Context.
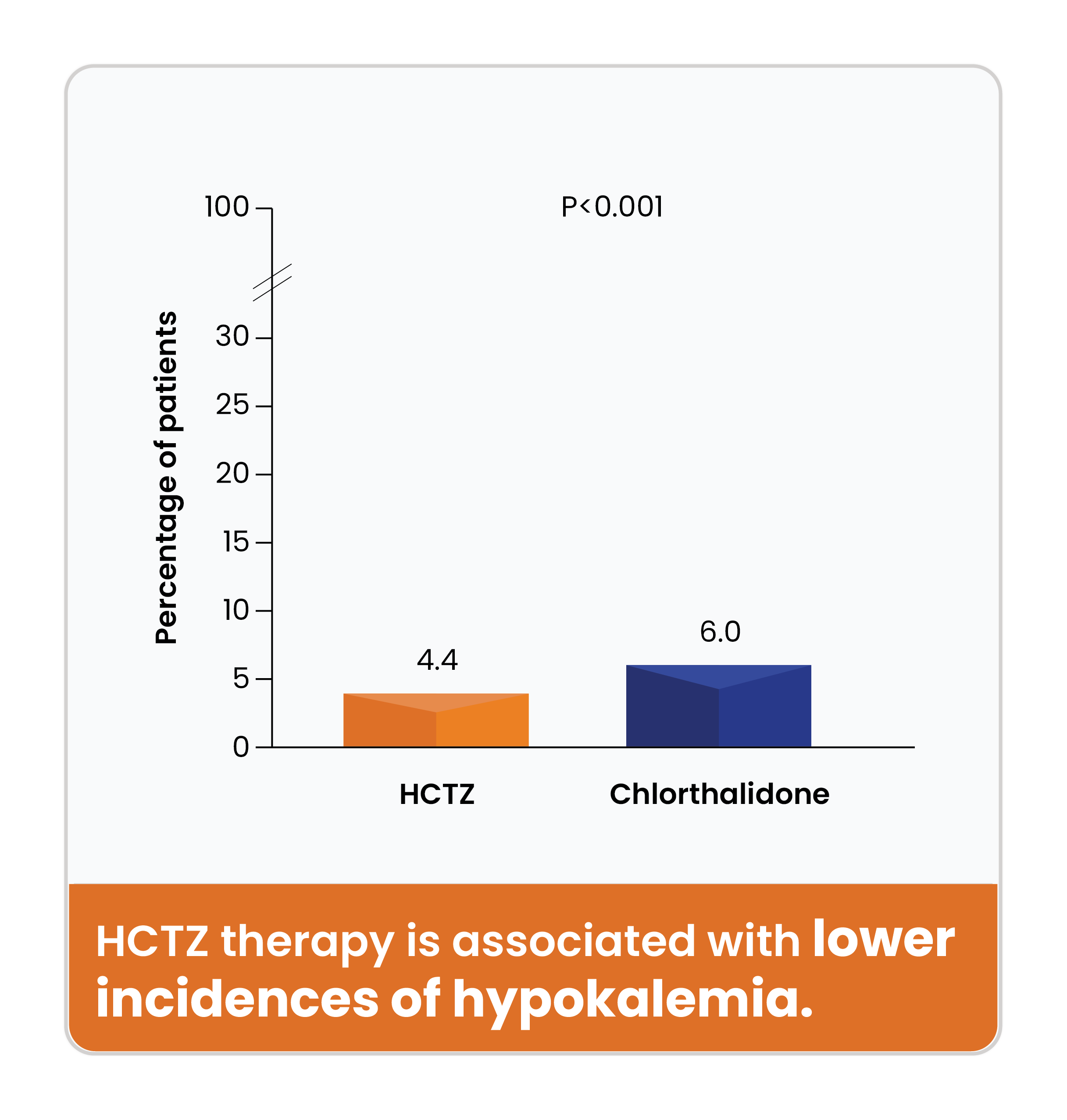
HCTZ therapy was associated with lower incidences of hypokalemia Compared to Chlorthalidone.
© 2024 Reassurance. All Rights Reserved by Reassurance